
Next, locate and select the Kali Linux ISO image you downloaded earlier and click on "OK." You need to access the settings by clicking on the "Settings" button, choosing Storage tab, selecting "Empty" CD/DVD icon under "Controller: IDE" then selecting "Choose Virtual Optical Disk File" from the dropdown menu. Step 3 involves configuring the virtual machine you just created to boot from the Kali Linux ISO image you just downloaded. Allocating these will pave the way for the creation of a new VM. Select a recommended RAM minimum of 2 GB for Kali Linux and create a virtual hard drive of at least 20 GB. Step 2 is creating a brand new virtual machine in VirtualBox, by following a few straightforward steps, including giving your VM a name, choosing "Linux" as Type, and "Debian (64-bit)" as Version. Once downloaded, save it on your preferred location on the computer. Step 1 is getting the Kali Linux ISO image by downloading from the Kali Linux website where you can choose from various versions depending on your needs, lightweight or the full ISO image. Assuming you're familiar with the basic concepts such as virtualization, reading on will guide you through the nitty-gritty of bringing Kali Linux to VirtualBox.

To kick off your Kali Linux experience, installing it on a virtual machine through VirtualBox, a free and open-source virtualization software, is one of the simplest ways.
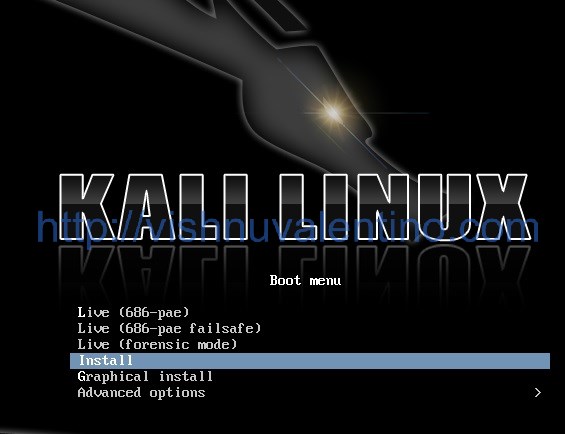
Kali Linux, a Linux distribution for cybersecurity pros and enthusiasts looking for a robust platform for security auditing and penetration testing, is a popular choice.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
